Reverse a Hex Number in C : If you are learning C programming, working with hexadecimal numbers is an important skill. One common task is to reverse a hex number – that means flipping its digits from last to first.Master the art of reversing a hexadecimal number with this beginner-friendly guide covering C++, Python, and Java. Learn what hex numbers are, how reversal works, and explore simple, step-by-step programs for each language. Perfect for students and programmers looking to practice string manipulation, number system basics, and improve problem-solving skills with real coding examples.
In this tutorial, we will explain what a hex number is, how reversing works, and how to write C code to reverse a hexadecimal number step-by-step.
What is a Hex Number?
A hexadecimal number (or hex number) is a number system with base 16.
It uses digits 0-9 and letters A-F:
Hex: 0, 1, 2, ..., 9, A, B, C, D, E, F
Decimal: 0, 1, 2, ..., 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15
Example:
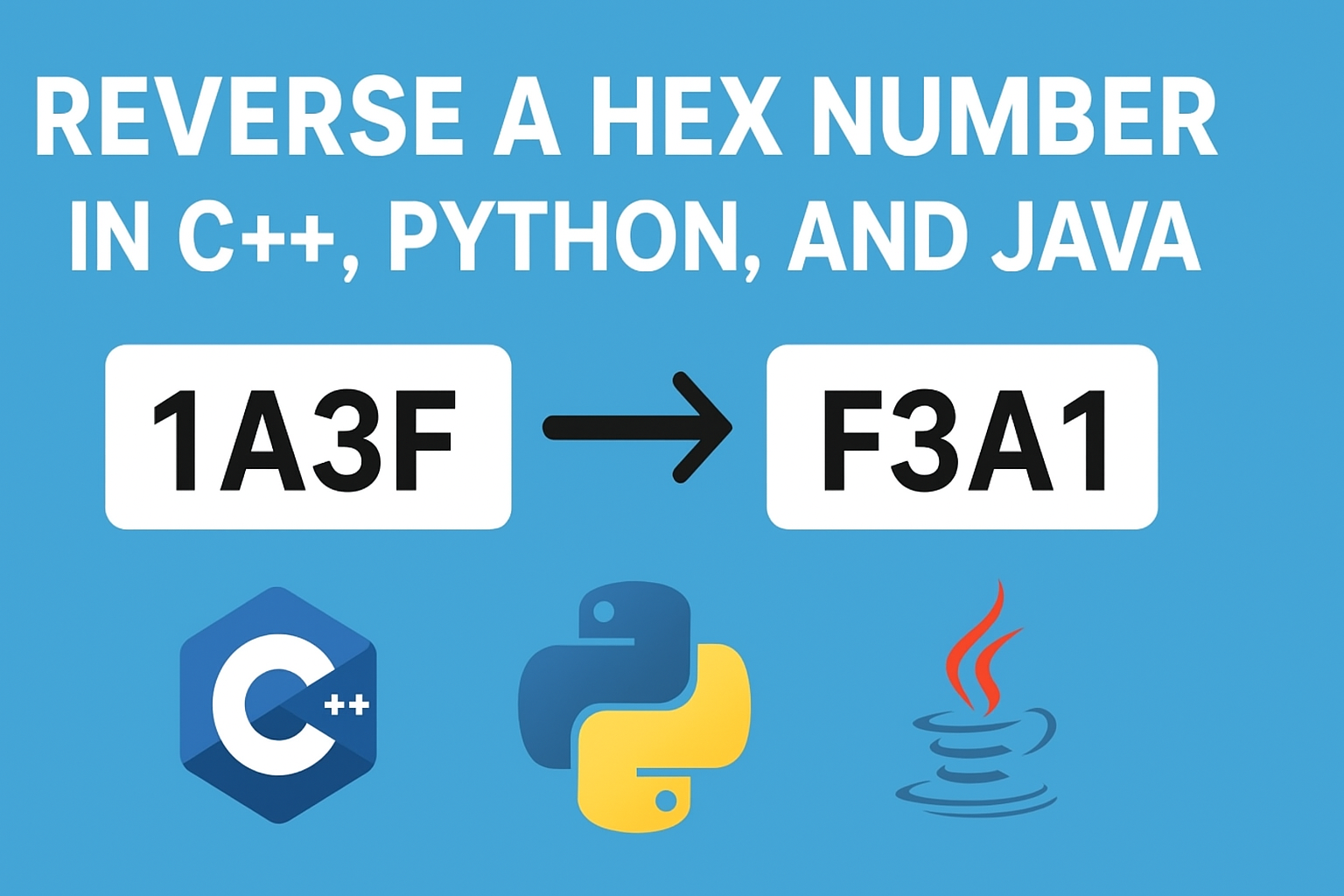
- Hex 1A3F in decimal is 6719.
What Does “Reverse a Hex Number” Mean?
Reversing a hex number means reading its hexadecimal digits from right to left.
Example:
Original: 1A3F
Reversed: F3A1
Steps to Reverse a Hex Number in C
We can reverse a hex number by:
- Reading the number as a string (so letters and numbers are preserved).
- Reversing the string by swapping characters.
- Printing the reversed hex number.
1.C Program to Reverse a Hex Number
#include
#include
int main() {
char hex[100]; // To store hex number as string
int length, i;
char temp;
// Step 1: Input hex number
printf("Enter a hexadecimal number: ");
scanf("%s", hex);
// Step 2: Find length
length = strlen(hex);
// Step 3: Reverse the string
for (i = 0; i < length / 2; i++) {
temp = hex[i];
hex[i] = hex[length - i - 1];
hex[length - i - 1] = temp;
}
// Step 4: Output the reversed hex number
printf("Reversed hexadecimal number: %s\n", hex);
return 0;
}
Example Output
Enter a hexadecimal number: 1A3F
Reversed hexadecimal number: F3A1
How Reverse a Hex Number Code Works
- We store the hex number as a string to preserve both numbers and letters.
strlen()helps us find how many characters are in the input.- A loop swaps characters from start and end until the middle is reached.
- Finally, we print the reversed result.
Key Points of Reverse a Hex Number
- Use
char[]to store hex numbers with letters. - Always handle input as a string, not as an integer, when reversing.
- Works for both uppercase (
A-F) and lowercase (a-f) hex letters.
2. Reverse a Hex Number in C++
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
string hexNum;
// Step 1: Input hex number
cout << "Enter a hexadecimal number: ";
cin >> hexNum;
// Step 2: Reverse the string
reverse(hexNum.begin(), hexNum.end());
// Step 3: Output reversed hex
cout << "Reversed hexadecimal number: " << hexNum << endl;
return 0;
}
Explanation:
- We use
stringto store the hex value. - The
reverse()function from - Works for both uppercase and lowercase letters.
3. Reverse a Hex Number in Python
# Step 1: Input hex number
hex_num = input("Enter a hexadecimal number: ")
# Step 2: Reverse the string using slicing
reversed_hex = hex_num[::-1]
# Step 3: Output result
print("Reversed hexadecimal number:", reversed_hex)
Explanation:
- Python treats strings as sequences, so slicing
[::-1]reverses the string easily. - This method is the shortest and beginner-friendly.
4. Reverse a Hex Number in Java
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ReverseHex {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// Step 1: Input hex number
System.out.print("Enter a hexadecimal number: ");
String hexNum = sc.next();
// Step 2: Reverse using StringBuilder
String reversedHex = new StringBuilder(hexNum).reverse().toString();
// Step 3: Output result
System.out.println("Reversed hexadecimal number: " + reversedHex);
sc.close();
}
}
Explanation:
- Java’s
StringBuilderclass has a built-inreverse()method. - Using
toString()converts the reversed object back into a string.
Example Run for Reverse a Hex Number in all Languages
Enter a hexadecimal number: 1A3F
Reversed hexadecimal number: F3A1
Key Takeaways
- Always store hex numbers as strings when reversing.
- C++ uses
reverse()from - Python uses slicing
[::-1]. - Java uses
StringBuilder.reverse().
FAQ : Reverse a Hex Number in C
Q1: What does it mean to reverse a hex number in C?
Ans: Reversing a hex number means rearranging its hexadecimal digits in reverse order. For example, reversing 0x1A3F gives 0xF3A1. This is often used in embedded systems and low-level programming.
Q2: How can I reverse a hex number in C?
Ans: You can reverse a hex number by extracting each digit using bitwise operations or string manipulation, and then reconstructing the number in reverse order.
Q3: Can I reverse a hex number using arrays or strings?
Ans: Yes! You can convert the hex number to a string, reverse the string, and convert it back to a number. This method is simple and beginner-friendly.
Q4: Is reversing a hex number different in C++ or Python?
Ans: The concept is the same across languages, but the implementation differs. In C++, you can use std::string for easy manipulation. In Python, you can use slicing to reverse the string representation of a hex number.
Q5: Why is reversing a hex number important in embedded systems?
Ans: Reversing hex numbers is useful in memory management, communication protocols, endianness handling, and debugging, where the byte order matters.
Q6: Are there any common mistakes to avoid when reversing hex numbers in C?
Ans: Common mistakes include ignoring leading zeros, not handling negative numbers correctly, and mixing up bitwise operations with string manipulation methods.
You can also Visit other tutorials of Embedded Prep
- Multithreading in C++
- Multithreading Interview Questions
- Multithreading in Operating System
- Multithreading in Java
- POSIX Threads pthread Beginner’s Guide in C/C++
- Speed Up Code using Multithreading
- Limitations of Multithreading
- Common Issues in Multithreading
- Multithreading Program with One Thread for Addition and One for Multiplication
- Advantage of Multithreading
- Disadvantages of Multithreading
- Applications of Multithreading: How Multithreading Makes Modern Software Faster and Smarter”
- Master CAN Bus Interview Questions 2025
- What Does CAN Stand For in CAN Bus?
- CAN Bus Message Filtering Explained
- CAN Bus Communication Between Nodes With Different Bit Rates
- How Does CAN Bus Handle Message Collisions
- Message Priority Using Identifiers in CAN Protocol
Mr. Raj Kumar is a highly experienced Technical Content Engineer with 7 years of dedicated expertise in the intricate field of embedded systems. At Embedded Prep, Raj is at the forefront of creating and curating high-quality technical content designed to educate and empower aspiring and seasoned professionals in the embedded domain.
Throughout his career, Raj has honed a unique skill set that bridges the gap between deep technical understanding and effective communication. His work encompasses a wide range of educational materials, including in-depth tutorials, practical guides, course modules, and insightful articles focused on embedded hardware and software solutions. He possesses a strong grasp of embedded architectures, microcontrollers, real-time operating systems (RTOS), firmware development, and various communication protocols relevant to the embedded industry.
Raj is adept at collaborating closely with subject matter experts, engineers, and instructional designers to ensure the accuracy, completeness, and pedagogical effectiveness of the content. His meticulous attention to detail and commitment to clarity are instrumental in transforming complex embedded concepts into easily digestible and engaging learning experiences. At Embedded Prep, he plays a crucial role in building a robust knowledge base that helps learners master the complexities of embedded technologies.