Complete QNX OS interview guide with beginner to advanced questions on RTOS, IPC, scheduling, drivers, debugging, and automotive systems.
QNX is widely used in safety-critical and real-time embedded systems such as automotive infotainment, ADAS, medical devices, and industrial automation. Preparing for a QNX interview requires much more than memorizing basic RTOS concepts it demands a deep understanding of microkernel architecture, message passing, real-time scheduling, device drivers, memory management, and system-level debugging.
This article provides a complete and structured set of QNX OS interview questions, carefully arranged from beginner to advanced level. Whether you are a fresher stepping into embedded systems or an experienced engineer working on automotive or safety-critical platforms, these questions will help you assess your knowledge, identify gaps, and prepare confidently for real-world QNX interviews.
Each section mirrors how QNX is actually used in production systems, making this guide practical, relevant, and industry-focused.
Why These QNX Interview Questions Are Useful
These questions are not random or theoretical. They are based on real interview patterns and day-to-day QNX development scenarios.
Here’s why this question set is genuinely useful:
- Covers the complete QNX ecosystem
From microkernel basics to advanced topics like adaptive partitioning, audio services, drivers, and safety isolation, nothing important is skipped. - Matches real interview progression
Interviews usually start with architecture and fundamentals, then move to IPC, scheduling, memory, drivers, and finally system design. This question flow follows the same pattern. - Builds strong conceptual clarity
Many engineers “use” QNX but struggle to explain why things work the way they do. These questions force you to think at system level, not just API level. - Helps freshers and experienced engineers alike
Beginners can start from the basics, while experienced candidates can focus on advanced debugging, performance tuning, audio, and safety-critical design. - Automotive and safety focused
QNX is heavily used in automotive. Topics like ISO 26262, ASIL, hypervisor, fault tolerance, and real-time guarantees are frequently asked and fully covered here. - Excellent self-assessment tool
If you can confidently explain most of these questions, you are interview-ready. If not, they clearly show where you need to revise.
In short, this question set prepares you not just to pass interviews, but to think like a QNX system engineer.
QNX OS Interview Questions
BASIC LEVEL : QNX Fundamentals
QNX Basics
- What is QNX?
- Is QNX a real-time operating system?
- What does “microkernel” mean in QNX?
- How is QNX different from Linux?
- Where is QNX commonly used?
- What are the main features of QNX?
- What does POSIX compliance mean in QNX?
- Is QNX open source or proprietary?
- What is Neutrino in QNX?
- What is deterministic behavior in RTOS?
- What is the latest version of QNX?
QNX Architecture
- Explain QNX architecture
- Explain QNX microkernel architecture.
- What runs in kernel space in QNX?
- What runs in user space in QNX?
- Why does QNX use message passing?
- What are resource managers in QNX?
- What is the role of the microkernel?
- How does QNX achieve fault tolerance?
- What is adaptive partitioning?
- What is a thread in QNX?
- What is a process in QNX?
For a detailed explanation of the answer, you can visit : QNX OS Interview Questions and Answer
BASIC : Boot & Startup
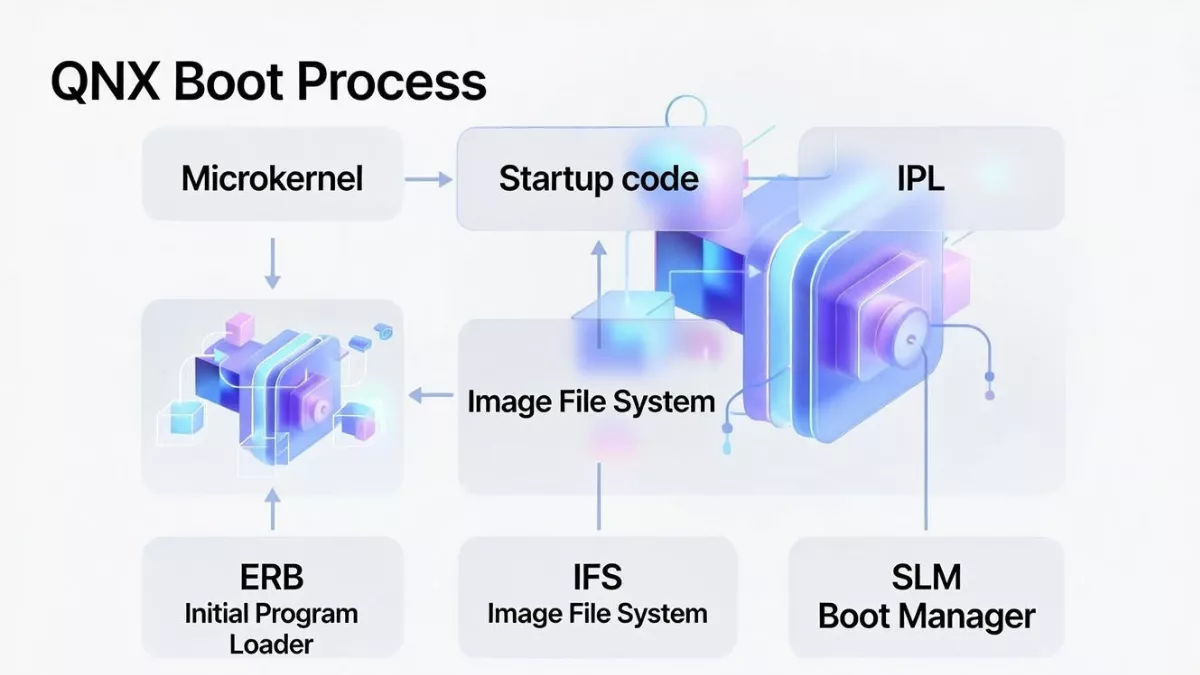
- What is the QNX boot sequence?
- What is IPL (Initial Program Loader)?
- What is IFS (Image File System)?
- What is startup code in QNX?
- What is the role of
procnto? - What is
io-pkt? - What is
devb-*? - What is
devc-*? - What is a startup script?
- Where are startup scripts located?
INTERMEDIATE : Process, Thread & Scheduling
Processes & Threads
- Difference between process and thread in QNX?
- What is the default thread scheduling policy?
- What is priority inheritance?
- What is priority inversion?
- How does QNX handle priority inversion?
- What is round-robin scheduling?
- What is FIFO scheduling?
- What is sporadic scheduling?
- What is adaptive scheduling?
- How many priority levels does QNX support?
Scheduling
- How does QNX guarantee real-time behavior?
- What happens if a high-priority thread blocks?
- How does QNX handle preemption?
- What is timeslice in QNX?
- What is thread affinity?
- How to bind threads to CPU cores?
- How does SMP work in QNX?
- How does QNX handle multicore systems?
- What is load balancing in QNX?
- What is interrupt latency?
INTERMEDIATE : IPC & Synchronization
IPC (Message Passing)
- Explain QNX message passing.
- What is
MsgSend()? - What is
MsgReceive()? - What is
MsgReply()? - What is synchronous vs asynchronous IPC?
- Why message passing is faster in QNX?
- What happens if a server crashes?
- How does QNX recover from server failure?
- What is pulse in QNX?
- What is a channel?
Synchronization
- What is a mutex?
- What is a semaphore?
- Difference between mutex and semaphore?
- What is condition variable?
- What is read-write lock?
- How does QNX avoid deadlocks?
- What is priority ceiling?
- What is priority inheritance mutex?
- What are atomic operations?
- How to synchronize ISRs with threads?
INTERMEDIATE : Memory Management
- How is memory managed in QNX?
- What is virtual memory?
- Does QNX support MMU?
- What is physical vs virtual address?
- What is shared memory?
- How to create shared memory in QNX?
- What is
mmap()? - What is memory partitioning?
- What is adaptive partitioning scheduler (APS)?
- How does QNX prevent memory starvation?
INTERMEDIATE : Signals, Timers & Interrupts
Signals
- What are signals in QNX?
- Difference between signals and pulses?
- How does QNX handle signals?
- What is
sigaction()? - What is signal masking?
Timers
- What is a timer in QNX?
- Difference between POSIX timer and QNX timer?
- What is
timer_create()? - What is a watchdog timer?
- How are timers implemented internally?
Interrupts
- What is ISR in QNX?
- How to attach an interrupt?
- What is
InterruptAttach()? - Difference between ISR and IST?
- What is interrupt latency?
- How does QNX handle nested interrupts?
- What is interrupt masking?
- What is pulse from ISR?
- Why ISR must be short?
- How does QNX handle interrupt priorities?
ADVANCED : Device Drivers & Resource Managers
Drivers
- What is a QNX device driver?
- Difference between Linux and QNX drivers?
- What is a resource manager?
- What is
resmgr_attach()? - What is
iofunc_*? - How does open/read/write work in QNX?
- What is pathname space?
- How does QNX handle
/dev? - What is
io-pktarchitecture? - What is
devbblock driver?
Character & Block Drivers
- How to write a character driver in QNX?
- How to write a block driver in QNX?
- How to expose hardware to user space?
- How does QNX handle DMA?
- How to handle interrupts in drivers?
- How to debug QNX drivers?
- What is driver hot-plug?
- What is
devctl()? - What is mount in QNX?
- How does filesystem driver work?
ADVANCED – Networking, Filesystem & Storage
Networking
- What is
io-pkt? - How TCP/IP stack works in QNX?
- Difference between QNX and Linux networking?
- What is socket API in QNX?
- How to debug network issues in QNX?
- What is PPS (Persistent Publish Subscribe)?
- What is Qnet?
- How IPC works across nodes?
- What is adaptive networking?
- How does QNX handle Ethernet drivers?
Filesystem
- What filesystems are supported in QNX?
- What is QNX6 filesystem?
- What is flash filesystem?
- What is wear leveling?
- What is power-safe filesystem?
- How does QNX handle journaling?
- What is fs-qnx6.so?
- How to mount filesystem at boot?
- What is
mountvsfstab? - How to debug filesystem issues?
EXPERT : Audio, Automotive & Safety
Audio (Very Important for Automotive)
- How ALSA works in QNX?
- Difference between Linux ALSA and QNX audio?
- What is PCM in QNX?
- What is mixer in QNX?
- What is audio routing?
- What is TDM?
- What is I2S in QNX?
- How audio service starts in QNX?
- How to debug audio latency issues?
- How to write a custom audio codec driver?
Automotive & Safety
- What is ASIL?
- How QNX supports functional safety?
- What is ISO 26262?
- What is safety partition?
- What is hypervisor in QNX?
- Difference between QNX Hypervisor and Linux?
- What is secure boot in QNX?
- What is trust zone usage in QNX?
- How to isolate safety-critical tasks?
- How QNX ensures freedom from interference?
EXPERT : Debugging, Performance & Optimization
Debugging
- How to debug QNX applications?
- What is
gdbin QNX? - What is
pdebug? - How to debug startup issues?
- How to debug boot failures?
- How to debug drivers?
- How to trace IPC?
- What is System Profiler?
- What is Momentics IDE?
- How to analyze thread states?
Performance
- How to reduce IPC latency?
- How to optimize scheduling?
- How to measure interrupt latency?
- How to reduce boot time?
- How to optimize memory usage?
- How to profile CPU usage?
- How to handle CPU starvation?
- How to debug deadlocks?
- How to detect priority inversion?
- How to tune APS parameters?
ARCHITECT / SYSTEM DESIGN LEVEL
- Design a fault-tolerant QNX system.
- Design an audio service architecture in QNX.
- Design multi-core scheduling for QNX.
- Design safe OTA update mechanism in QNX.
- Design driver recovery without reboot.
- Design IPC between safety and non-safety domains.
- Design fast boot system in QNX.
- Design logging framework in QNX.
- Design watchdog strategy.
- Design startup dependency ordering.
BONUS : REAL INTERVIEW SCENARIO QUESTIONS
- Why did you choose QNX over Linux?
- How do you debug a hung QNX system?
- How do you recover from driver crash?
- How do you handle memory leaks in QNX?
- How do you ensure real-time guarantees?
- What challenges did you face in QNX?
- How do you debug race conditions?
- How do you handle CPU overload?
- How do you design high-availability service?
- Explain one QNX project you worked on.
Conclusion
QNX is not just another operating system — it is designed for systems where failure is not an option. That’s why interviewers expect more than surface-level knowledge. They look for engineers who understand real-time behavior, fault isolation, IPC, scheduling, drivers, and system reliability.
This comprehensive list of QNX OS interview questions is designed to help you build that understanding step by step. If you go through these questions honestly and study the areas where you feel weak, you won’t just memorize answers — you’ll gain confidence in how QNX actually works in real products.
Use this guide as:
- A revision checklist before interviews
- A learning roadmap for QNX
- A benchmark for your embedded systems knowledge
Mastering these concepts will not only help you clear QNX interviews, but also make you a stronger, more reliable embedded software engineer in real-world projects.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) : QNX OS Interview Preparation
1. What is QNX and why is it used in embedded systems?
QNX is a real-time operating system (RTOS) based on a microkernel architecture. It is widely used in embedded systems because it offers deterministic performance, high reliability, fault isolation, and strong support for safety-critical applications such as automotive infotainment, ADAS, medical devices, and industrial automation.
2. Is QNX difficult to learn for beginners?
QNX can feel challenging at first, especially if you are new to RTOS concepts. However, if you already understand C/C++, processes, threads, and basic OS concepts, learning QNX becomes much easier. Starting with microkernel fundamentals and message passing helps build a strong foundation.
3. How is QNX different from Linux?
Linux uses a monolithic kernel where most services run in kernel space, while QNX follows a microkernel approach. In QNX, drivers, filesystems, and network stacks run in user space, which improves fault tolerance and system stability—an important requirement for safety-critical systems.
4. Why is message passing important in QNX?
Message passing is the core IPC mechanism in QNX. It enables safe, deterministic communication between processes and threads. Because services run in user space, message passing ensures isolation while still delivering high performance and real-time guarantees.
5. What topics are most important for a QNX interview?
Interviewers usually focus on:
- Microkernel architecture
- IPC (MsgSend, MsgReceive, pulses)
- Thread scheduling and priorities
- Memory management
- Interrupt handling
- Resource managers and device drivers
- Debugging and performance tuning
- Automotive and safety concepts (ISO 26262, ASIL)
6. Are QNX interview questions more theoretical or practical?
Most QNX interviews are practical and scenario-based. Interviewers often ask how you debug issues, design fault-tolerant services, handle priority inversion, or recover from driver failures rather than just theoretical definitions.
7. Is QNX mainly used in automotive projects?
Automotive is the largest user of QNX today, especially for infotainment and digital cockpits. However, QNX is also widely used in medical devices, railway systems, industrial controllers, networking equipment, and aerospace applications.
8. Do I need driver development experience to clear a QNX interview?
Driver knowledge is not mandatory for entry-level roles, but it is a big advantage for experienced positions. Understanding resource managers, interrupt handling, and user-space drivers significantly improves your interview performance.
9. How should I prepare for advanced QNX interview rounds?
For advanced rounds, focus on:
- Real-time scheduling policies
- Adaptive partitioning (APS)
- IPC performance tuning
- Debugging tools (GDB, Momentics, System Profiler)
- Multicore and SMP behavior
- System design and fault recovery strategies
10. Are QNX interviews harder than Linux embedded interviews?
QNX interviews are usually more system-design oriented and focus heavily on real-time behavior and reliability. While Linux interviews test kernel and driver knowledge, QNX interviews test how well you understand deterministic systems and fault isolation.
11. Can these QNX interview questions help in real projects?
Yes. These questions are not just for interviews. They help you understand how QNX systems behave in real products, how services communicate, how failures are handled, and how performance is optimized—skills that are directly applicable to real-world projects.
12. What level of C/C++ knowledge is required for QNX?
A solid understanding of C is essential, and C++ is commonly used for application and service development. Knowledge of pointers, memory management, multithreading, and synchronization primitives is critical for working effectively with QNX.
13. How long does it take to prepare for a QNX interview?
Preparation time depends on your background. Freshers may need 6–8 weeks, while experienced embedded engineers can revise and prepare in 2–3 weeks by focusing on QNX-specific concepts and practical scenarios.
14. Is QNX still relevant in 2026 and beyond?
Yes. QNX continues to be a key platform for safety-critical and automotive systems. With the growth of software-defined vehicles and real-time computing, QNX remains highly relevant.
15. How should I use this QNX interview question guide effectively?
Go through the questions section by section. Try to explain each answer in your own words. Wherever you struggle, revise that topic and relate it to real scenarios. This approach will build confidence and improve both interview performance and practical understanding.
Read More about Process : What is is Process
Read More about System Call in Linux : What is System call
Read More about IPC : What is IPC
Mr. Raj Kumar is a highly experienced Technical Content Engineer with 7 years of dedicated expertise in the intricate field of embedded systems. At Embedded Prep, Raj is at the forefront of creating and curating high-quality technical content designed to educate and empower aspiring and seasoned professionals in the embedded domain.
Throughout his career, Raj has honed a unique skill set that bridges the gap between deep technical understanding and effective communication. His work encompasses a wide range of educational materials, including in-depth tutorials, practical guides, course modules, and insightful articles focused on embedded hardware and software solutions. He possesses a strong grasp of embedded architectures, microcontrollers, real-time operating systems (RTOS), firmware development, and various communication protocols relevant to the embedded industry.
Raj is adept at collaborating closely with subject matter experts, engineers, and instructional designers to ensure the accuracy, completeness, and pedagogical effectiveness of the content. His meticulous attention to detail and commitment to clarity are instrumental in transforming complex embedded concepts into easily digestible and engaging learning experiences. At Embedded Prep, he plays a crucial role in building a robust knowledge base that helps learners master the complexities of embedded technologies.