I2C Bus on Linux beginner-friendly guide with advantages, disadvantages, applications, and FAQs for embedded systems and IoT projects.
If you are starting your journey in embedded systems or Linux device drivers, you will often come across the term I2C bus. It plays a major role in connecting sensors, displays, and other peripheral devices to Linux-based systems like Raspberry Pi, BeagleBone, or custom embedded boards. Let’s break it down in a beginner-friendly way.
What is the I2C Bus?
I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit) is a two-wire communication protocol used to connect low-speed devices to processors or microcontrollers. It only uses:
- SDA (Serial Data Line) – for data transfer
- SCL (Serial Clock Line) – for synchronization
This simplicity makes it perfect for embedded systems where multiple devices need to communicate with the CPU without requiring many pins.
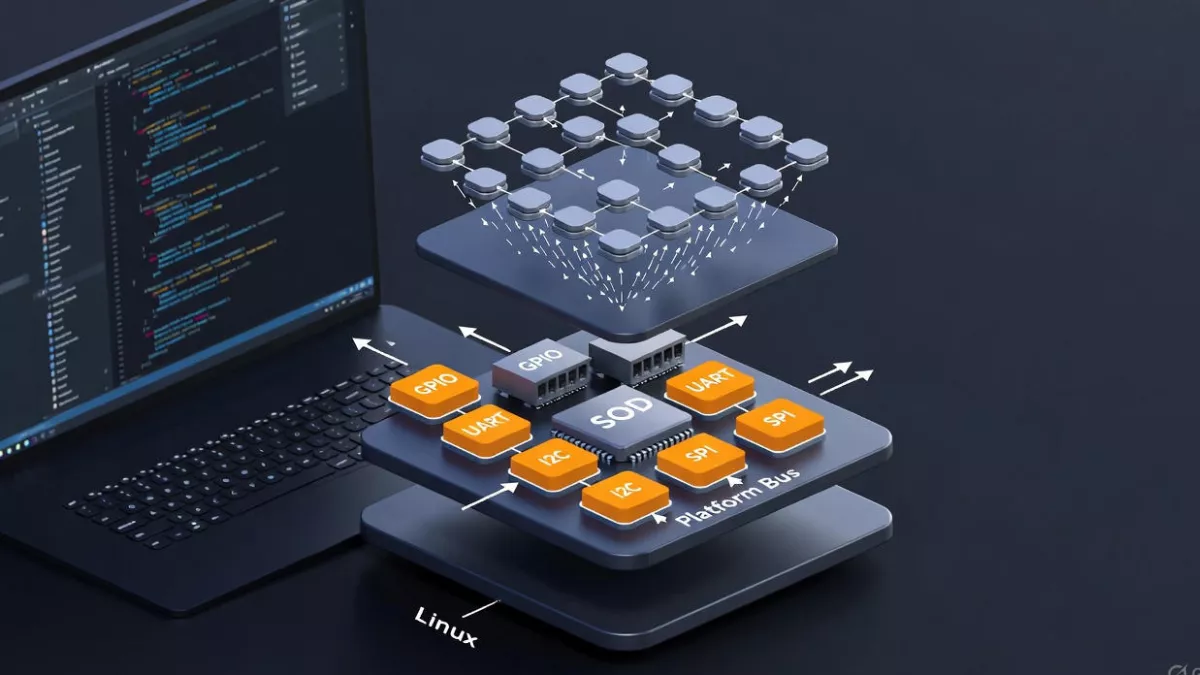
How I2C Works in Linux
Linux has built-in support for I2C. You can interact with devices connected over I2C through:
- Kernel Drivers – Device drivers provide higher-level access.
- User Space Tools – Linux offers command-line utilities to check and communicate with I2C devices.
Common I2C Tools in Linux
i2cdetect– Scan and detect I2C devices connected to your system.i2cget– Read data from a device register.i2cset– Write data to a device register.i2cdump– Dump all registers of an I2C device.
These commands are part of the i2c-tools package, which you can install on most Linux distributions.
Real-World Example
Imagine you have a temperature sensor connected via I2C to a Raspberry Pi.
- You run
i2cdetect -y 1to find its address. - Then use
i2cgetto read the sensor’s register values. - Finally, you can display the temperature on a screen or log it into a file.
This makes I2C very popular in IoT projects, robotics, and automotive systems.
Advantages of Using I2C on Linux
Simple two-wire communication
Supports multiple devices on the same bus
Built-in Linux support with tools and drivers
Widely used in embedded and industrial applications
Disadvantages of I2C Bus on Linux
Limited Speed – I2C is slower compared to SPI or UART.
Short Distance Communication – It works best for short distances (within a board).
Complexity with Many Devices – The more devices you connect, the higher the risk of address conflicts.
Power Consumption – Pull-up resistors increase power usage in some cases.
Applications of I2C Bus on Linux
The I2C Bus on Linux is widely used in real-world projects:
- IoT Devices – connecting temperature sensors, humidity sensors, and motion detectors.
- Display Modules – driving small OLED or LCD screens.
- Embedded Boards – BeagleBone, Raspberry Pi, and STM32 projects.
- Automotive Systems – reading sensor data in Linux-based automotive ECUs.
- Industrial Monitoring – logging pressure, temperature, and humidity in factories.
Conclusion
The I2C bus on Linux is a beginner-friendly communication method that allows easy connection of multiple devices using only two wires. Whether you’re working on a Raspberry Pi project, BeagleBone board, or professional embedded platform, learning I2C will help you connect sensors, displays, and other peripherals effortlessly.
If you are just starting out, experiment with the i2c-tools package and try scanning and reading from a real sensor. It’s one of the best ways to get hands-on experience with Linux hardware communication.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on I2C Bus on Linux
1. What is the I2C Bus on Linux?
The I2C Bus on Linux is a two-wire communication system used to connect multiple devices like sensors, displays, and chips to Linux-based boards. Linux provides built-in drivers and tools to scan, read, and write data over the I2C bus.
2. How do I check I2C devices in Linux?
You can use the i2c-tools package. The most common command is:
i2cdetect -y 1
This will scan the I2C bus and show connected devices with their addresses.
3. What are the advantages of using I2C Bus on Linux?
- Requires only two wires (SDA & SCL)
- Supports multiple devices on the same bus
- Easy to use with built-in Linux support
- Widely used in embedded and IoT applications
4. What are the disadvantages of I2C Bus on Linux?
- Slower compared to SPI or UART
- Best for short-distance communication only
- Possible address conflicts when many devices are connected
- Slightly higher power consumption due to pull-up resistors
5. What are common applications of I2C Bus on Linux?
I2C is used in Raspberry Pi projects, BeagleBone boards, STM32 microcontrollers, and more. Applications include reading sensor data (temperature, humidity, motion), driving OLED/LCD displays, IoT projects, and automotive systems.
6. Which Linux tools are used for I2C communication?
The most common tools are:
i2cdetect– scans devicesi2cget– reads data from a devicei2cset– writes data to a devicei2cdump– dumps register values
7. Can I use I2C on Raspberry Pi with Linux?
Yes. Raspberry Pi has built-in support for I2C. After enabling it in the Raspberry Pi configuration, you can use i2c-tools to communicate with connected devices.
Mr. Raj Kumar is a highly experienced Technical Content Engineer with 7 years of dedicated expertise in the intricate field of embedded systems. At Embedded Prep, Raj is at the forefront of creating and curating high-quality technical content designed to educate and empower aspiring and seasoned professionals in the embedded domain.
Throughout his career, Raj has honed a unique skill set that bridges the gap between deep technical understanding and effective communication. His work encompasses a wide range of educational materials, including in-depth tutorials, practical guides, course modules, and insightful articles focused on embedded hardware and software solutions. He possesses a strong grasp of embedded architectures, microcontrollers, real-time operating systems (RTOS), firmware development, and various communication protocols relevant to the embedded industry.
Raj is adept at collaborating closely with subject matter experts, engineers, and instructional designers to ensure the accuracy, completeness, and pedagogical effectiveness of the content. His meticulous attention to detail and commitment to clarity are instrumental in transforming complex embedded concepts into easily digestible and engaging learning experiences. At Embedded Prep, he plays a crucial role in building a robust knowledge base that helps learners master the complexities of embedded technologies.