Discover what is a trap and interrupt in OS, their key differences, types, examples, and advantages explained clearly for easy understanding.
Ever wondered what is a trap and interrupt in operating systems? Learn the real difference between a trap and interrupt, their types, advantages, disadvantages, and real-life examples — explained simply and SEO-friendly for your understanding.
Let’s Start with the Basics: What Is a Trap and Interrupt?
Imagine you’re sipping coffee while your computer multitasks smoothly — running apps, downloading files, and playing music. Behind that magic lies something called traps and interrupts.
So, what is a trap and interrupt?
In simple terms, both are signals that make the CPU pause what it’s doing to handle something more urgent.
- A trap is a software-generated interrupt — triggered intentionally by a program when something unexpected happens (like dividing by zero).
- An interrupt, on the other hand, is a hardware signal — sent by an external device (like a keyboard or mouse) to get the CPU’s attention.
Understanding What Is a Trap in OS
Let’s dig deeper into what is a trap.
A trap is an internal signal sent to the operating system when an error or special condition occurs in a program.
Think of it like a polite “excuse me” from your software to the OS — asking for help when it hits a problem.
Common examples of traps:
- Division by zero
- Invalid memory access
- System call (like requesting file access)
- Breakpoints for debugging
When you understand what is a trap and interrupt, you realize that a trap isn’t a bad thing. It’s actually how programs safely communicate with the OS when something goes off track.
What Is an Interrupt in OS?
Now that we’ve covered traps, let’s talk about what is an interrupt.
An interrupt is a signal sent by hardware to tell the CPU to stop its current task and handle an urgent event.
Picture this: You’re typing on your keyboard. Each keystroke generates an interrupt that tells the CPU — “Hey, process this input right now!”
Types of Interrupts:
- Hardware Interrupts: Generated by devices like keyboards, network cards, or timers.
- Software Interrupts: Triggered by programs (though these are sometimes referred to as traps).
So, in short, what is a trap and interrupt — traps come from software, interrupts come from hardware.
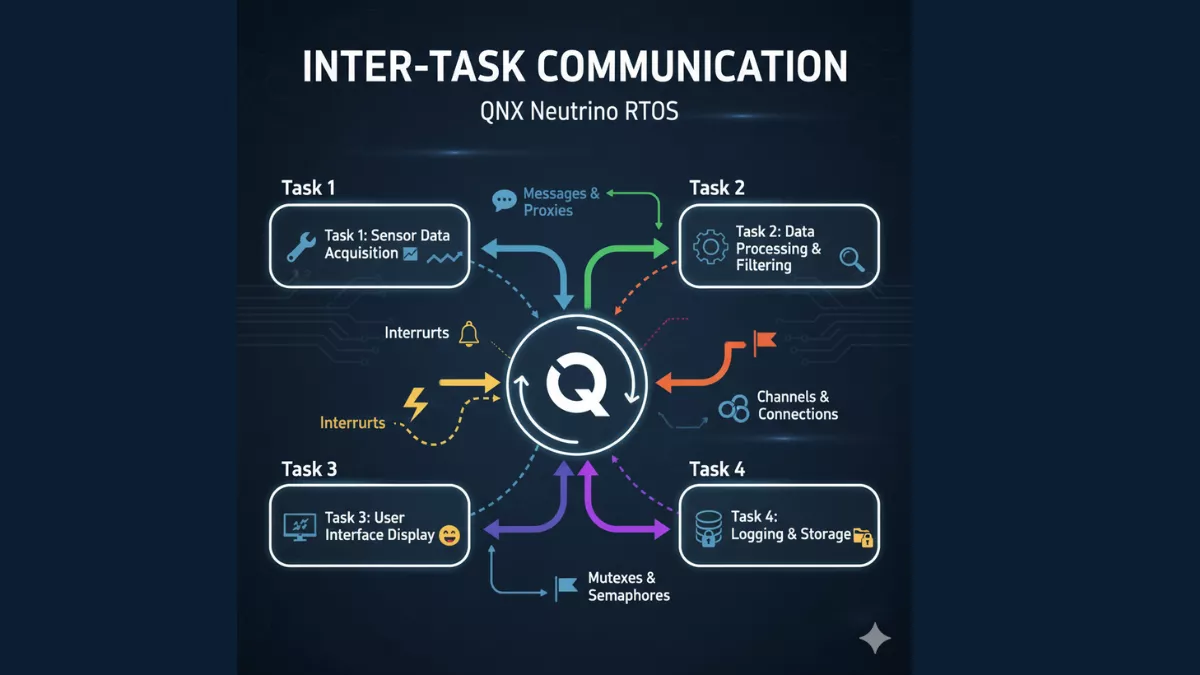
Key Difference Between Trap and Interrupt
Let’s compare the two clearly — because when you search what is a trap and interrupt, this is what really matters:
| Feature | Trap | Interrupt |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Software (internal) | Hardware (external) |
| Purpose | Handles errors or system calls | Handles device or external events |
| Example | Division by zero, system call | Keyboard input, I/O completion |
| Detects | Software anomalies | External device requests |
| Occurs | Synchronously (predictable) | Asynchronously (unpredictable) |
Now, when someone asks you what is a trap and interrupt, you can confidently explain both without confusion.
Advantages of Traps and Interrupts
Understanding what is a trap and interrupt also means knowing their benefits:
Advantages:
- Efficient CPU utilization — no time wasted on polling devices.
- Immediate error handling through traps.
- Improves system responsiveness.
- Supports multitasking and real-time performance.
Disadvantages of Traps and Interrupts
Nothing’s perfect, right? So while what is a trap and interrupt improves performance, there are a few downsides:
Disadvantages:
- Complex handling mechanism.
- Debugging interrupt-driven systems can be tricky.
- Priority conflicts between multiple interrupts.
- Increased system overhead due to frequent context switching.
Real-Life Example: Trap vs Interrupt
Let’s see what is a trap and interrupt in action.
Trap Example:
You run a program that tries to divide a number by zero — the CPU detects it and raises a trap, transferring control to the Operating system to handle the error gracefully.
Interrupt Example:
You plug in a USB drive. The hardware sends an interrupt to notify the OS that new hardware is connected.
Simple, right? That’s the beauty of understanding what is a trap and interrupt — it’s all about communication between the CPU, OS, and devices.
Summary: What Is a Trap and Interrupt in One Line
- Trap: Software-generated, synchronous signal for errors or system calls.
- Interrupt: Hardware-generated, asynchronous signal for external events.
So, the next time you read what is a trap and interrupt, just remember:
“Trap happens inside the program; interrupt comes from outside.”
Real-World Applications
Knowing what is a trap and interrupt helps developers and engineers in areas like:
- Operating system design
- Embedded systems
- Real-time processing
- Device driver development
For example, in embedded systems, interrupts manage sensors or input signals, while traps handle faults or system calls internally. To understand more about system performance issues related to interrupts and traps, check out When Does Thrashing Occur?.
C++ Example for Better Understanding
Here’s a small simulation to visualize what is a trap and interrupt conceptually:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void divideNumbers(int a, int b) {
try {
if (b == 0) {
throw "Trap: Division by zero!";
}
cout << "Result: " << a / b << endl;
} catch (const char* msg) {
cout << msg << endl;
}
}
void keyboardInterrupt() {
cout << "Interrupt: Keyboard input detected!" << endl;
}
int main() {
divideNumbers(10, 0); // Generates a software trap
keyboardInterrupt(); // Simulates a hardware interrupt
return 0;
}
This simple code demonstrates what is a trap and interrupt — the trap comes from within the code (software), while the interrupt mimics an external event.
FAQs on What Is a Trap and Interrupt
Q1. What is a trap and interrupt in OS?
A trap is a software-generated signal for errors or system calls, while an interrupt is a hardware signal indicating external events.
Q2. Is a trap synchronous or asynchronous?
A trap is synchronous because it happens as a direct result of program execution.
Q3. Are system calls traps or interrupts?
System calls are implemented using traps, since they’re triggered by software.
Q4. Can traps and interrupts occur together?
Yes, a system can handle multiple traps and interrupts at the same time, based on priority.
Final Thoughts
So, to wrap up — what is a trap and interrupt isn’t just an academic concept. It’s the foundation of how your computer communicates and handles events efficiently.
Next time your computer responds instantly to a key press or gracefully handles a crash, remember: that’s traps and interrupts silently doing their job
Mr. Raj Kumar is a highly experienced Technical Content Engineer with 7 years of dedicated expertise in the intricate field of embedded systems. At Embedded Prep, Raj is at the forefront of creating and curating high-quality technical content designed to educate and empower aspiring and seasoned professionals in the embedded domain.
Throughout his career, Raj has honed a unique skill set that bridges the gap between deep technical understanding and effective communication. His work encompasses a wide range of educational materials, including in-depth tutorials, practical guides, course modules, and insightful articles focused on embedded hardware and software solutions. He possesses a strong grasp of embedded architectures, microcontrollers, real-time operating systems (RTOS), firmware development, and various communication protocols relevant to the embedded industry.
Raj is adept at collaborating closely with subject matter experts, engineers, and instructional designers to ensure the accuracy, completeness, and pedagogical effectiveness of the content. His meticulous attention to detail and commitment to clarity are instrumental in transforming complex embedded concepts into easily digestible and engaging learning experiences. At Embedded Prep, he plays a crucial role in building a robust knowledge base that helps learners master the complexities of embedded technologies.