Discover the advantages of a multiprocessor system faster performance, higher throughput, reliability, and efficient parallel processing explained
So, you ask: what are the advantages of a multiprocessor system? Let’s dive in. Imagine you’ve got more than one brain in your computer, and those brains work together. That’s essentially what a multiprocessor system is. When you build something with two or more processors working in tandem, you unlock benefits you simply can’t get from a single-processor machine.
Here are the real advantages of a multiprocessor system — explained simply, no fluff.
1. Faster Execution & Better Performance
One big benefit: the advantage of a multiprocessor system is that tasks get done quicker. Since multiple processors can share the workload, systems that exploit multiprocessor architecture show higher throughput. Research shows multiplexed processor systems improve speed and reduce delays. (TechTarget)
So when you ask what are the advantages of a multiprocessor system, remember: speed and performance jump.
2. Increased Throughput
Closely related: the advantage of a multiprocessor system is higher throughput — more jobs done per unit time. When each processor can handle different processes, you don’t wait for one to finish before the next starts. (TutorialsPoint)
In plain talk: if you’ve got more processors, you can do more stuff at once.
3. Greater Reliability / Fault Tolerance
Another of the advantages of a multiprocessor system: resiliency. If one processor fails, others can take over (to some degree), so your system doesn’t crash entirely. (TutorialsPoint)
So you get a system that carries on rather than halts. That’s peace of mind.
4. Efficient Resource Sharing
The advantage of a multiprocessor system also lies in efficient use of resources. Memory, I/O devices, disks — in a shared-memory multiprocessor system, these can be used more economically. (TutorialsPoint)
So in effect you’re getting more bang for your hardware investment.
5. Scalability
When you want to grow your system, one of the advantages of a multiprocessor system is better scalability. You can add processors (depending on architecture) rather than replace the whole system. (ITU Online IT Training)
If tomorrow you need to handle bigger workloads, a multiprocessor architecture helps.
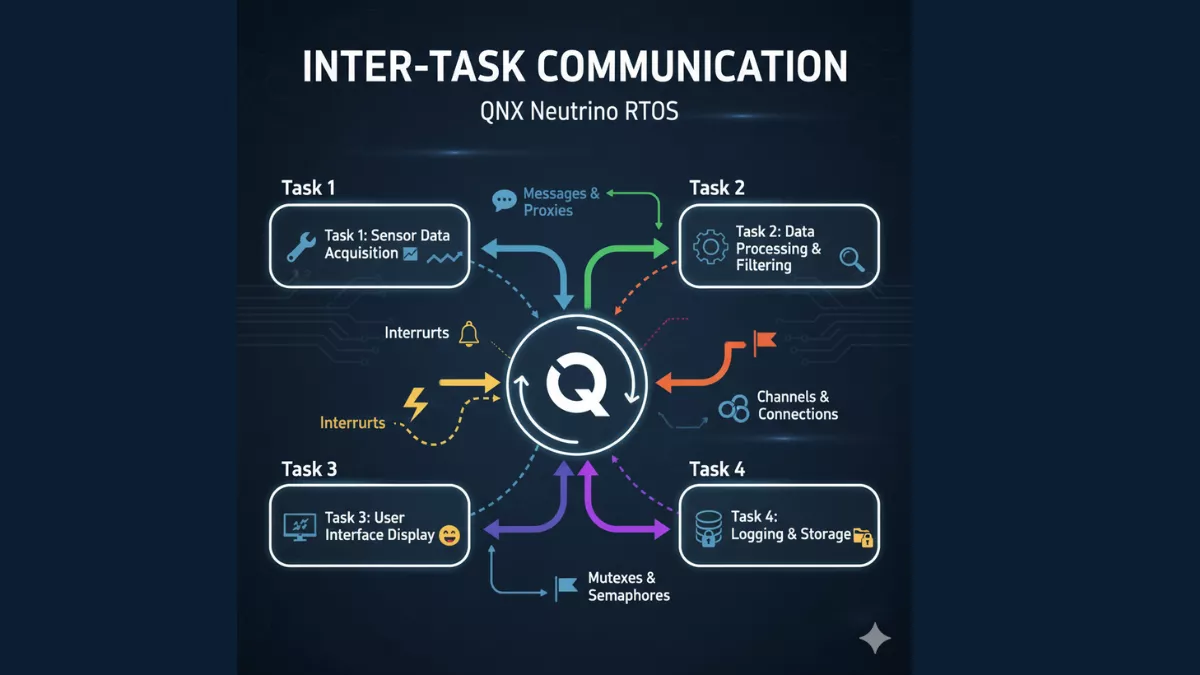
6. Parallel Processing Capabilities
The advantage of a multiprocessor system: the ability to truly run parallel processing. Multiple instructions, multiple data streams — this is a hallmark of multiprocessor systems. (Scaler)
That means faster data crunching, better for jobs like simulations, analytics, or big server tasks.
7. Better Utilization of System Components
Because of the advantage of a multiprocessor system, your system’s parts — memory, buses, etc. — get used more fully rather than idle. It’s not just “more processors” but “processors plus supporting hardware” working smarter together. (GeeksforGeeks)
8. Economic Over Time (In Some Cases)
Another point: one of the advantages of a multiprocessor system is cost-effectiveness in certain scenarios. Although initial cost may be higher, by sharing memory, storage, I/O you may get lower total cost than many separate single-processor machines. (TutorialsPoint)
So if you’re running many tasks, this model can save money long-term.
9. Better for High-Intensity Workloads
If you’ve got heavy workloads (servers, scientific computing, database systems) then one of the advantages of a multiprocessor system is that it handles peak demand better. (ITU Online IT Training)
So for “big jobs” a multiprocessor system makes a lot of sense.
Why This Matters to You
Okay, you might be thinking: “Great, cool tech talk, but why do I care?” Here’s the deal — if you’re choosing hardware, designing systems, or just trying to understand why some servers or hardware cost more — knowing what are the advantages of a multiprocessor system helps you make smarter decisions.
If you’re curious about how this concept compares to multiprogramming, check out this detailed guide on Multiprogramming in OS — it explains how operating systems handle multiple programs efficiently, which ties closely to how multiprocessor systems manage multiple processes.
- If you have many users, many independent tasks, or high-availability demands: pick a multiprocessor system.
- If your workload is small, single-threaded, and light: the extra complexity might not be worth it.
- If you anticipate growth or peaks: scalability becomes a big plus.
- If reliability is important (minimal downtime): then the advantage of a multiprocessor system really shines.
A Friendly Wrap-Up
So, in short: if you’re wondering what are the advantages of a multiprocessor system, remember — you’re looking at higher performance, more tasks done, better fault tolerance, efficient hardware use, scalability, and long-term cost benefits (in many cases).
It’s like having a team instead of a solo worker: multiple processors working in sync, handling many jobs, backing each other up, sharing the load. That’s your multiprocessor system advantage.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on Advantages of a Multiprocessor System
1. What are the main advantages of a multiprocessor system?
The main advantages of a multiprocessor system include faster processing speed, better performance, improved reliability, and efficient use of system resources. Since multiple processors share tasks, the system can handle more work in less time. Simply put, the advantage of a multiprocessor system is that everything runs smoother and faster.
2. How does a multiprocessor system improve performance?
The advantage of a multiprocessor system is that it divides tasks among processors. This parallel processing approach lets each processor handle different instructions simultaneously, increasing overall system throughput. Think of it as multiple chefs cooking different dishes at the same time — the meal gets done quicker.
3. Is reliability one of the advantages of a multiprocessor system?
Yes, reliability is a huge advantage of a multiprocessor system. If one processor fails, others can take over its tasks, reducing downtime. This fault-tolerant design is why multiprocessor architectures are often used in servers, aerospace systems, and mission-critical applications.
4. How does a multiprocessor system enhance throughput?
One of the most important advantages of a multiprocessor system is increased throughput. Since each processor can execute separate programs or threads, the system completes more jobs per second. This is why data centers and large-scale computing environments love multiprocessor setups.
5. Are multiprocessor systems cost-effective?
While the initial cost is higher, one long-term advantage of a multiprocessor system is better cost efficiency. Instead of running several single-processor machines, one multiprocessor system can handle all workloads efficiently, saving energy and maintenance costs over time.
6. How does scalability relate to the advantages of a multiprocessor system?
Scalability is one of the key advantages of a multiprocessor system. As demand grows, more processors can be added without replacing the entire system. It’s like upgrading your team instead of rebuilding your company from scratch — flexible and smart.
7. What types of tasks benefit most from a multiprocessor system?
Tasks that involve heavy computation — like simulations, data analytics, AI model training, and video rendering — benefit the most. The advantage of a multiprocessor system in these cases is that parallel execution drastically reduces processing time.
8. How is a multiprocessor system different from a multicore system?
Good question! While both allow parallel processing, the difference lies in hardware. A multiprocessor system uses multiple physical CPUs, whereas a multicore system has multiple cores within a single CPU. Still, the core advantage of a multiprocessor system remains — better performance, scalability, and fault tolerance.
9. Does a multiprocessor system use shared memory?
Yes, most multiprocessor systems use a shared memory model. One big advantage of a multiprocessor system is that processors can access the same memory pool, allowing faster data exchange and better resource sharing between tasks.
10. Are there any disadvantages of a multiprocessor system?
Sure, nothing’s perfect. Even though the advantages of a multiprocessor system are many, they come with challenges — like higher cost, complex design, and potential synchronization issues. But for high-performance applications, the pros usually outweigh the cons.
11. Why are multiprocessor systems used in servers?
The biggest advantage of a multiprocessor system in servers is handling multiple client requests simultaneously. When thousands of users hit a server at once, multiple processors make sure responses stay fast and reliable without crashes or slowdowns.
12. Can a multiprocessor system run multiple operating systems?
Yes, in some configurations, a multiprocessor system can run different OS instances or virtual machines. The advantage of a multiprocessor system in this setup is that each processor can handle its own workload without bottlenecks.
13. How do multiprocessor systems help in AI and machine learning?
In AI/ML, massive datasets and matrix operations need heavy computation. One practical advantage of a multiprocessor system is faster model training through distributed processing. It helps you crunch numbers faster, leading to quicker insights.
14. Are multiprocessor systems suitable for home computers?
Not always. The advantage of a multiprocessor system is best realized in high-end environments like servers, workstations, and cloud data centers. For most home users, multicore processors do the job well enough.
15. What’s the future of multiprocessor systems?
The future looks bright! With rising demand for high-speed computing, cloud platforms, and AI workloads, the advantages of a multiprocessor system are becoming even more relevant. Expect systems to become more power-efficient and even smarter at managing loads across processors.
Mr. Raj Kumar is a highly experienced Technical Content Engineer with 7 years of dedicated expertise in the intricate field of embedded systems. At Embedded Prep, Raj is at the forefront of creating and curating high-quality technical content designed to educate and empower aspiring and seasoned professionals in the embedded domain.
Throughout his career, Raj has honed a unique skill set that bridges the gap between deep technical understanding and effective communication. His work encompasses a wide range of educational materials, including in-depth tutorials, practical guides, course modules, and insightful articles focused on embedded hardware and software solutions. He possesses a strong grasp of embedded architectures, microcontrollers, real-time operating systems (RTOS), firmware development, and various communication protocols relevant to the embedded industry.
Raj is adept at collaborating closely with subject matter experts, engineers, and instructional designers to ensure the accuracy, completeness, and pedagogical effectiveness of the content. His meticulous attention to detail and commitment to clarity are instrumental in transforming complex embedded concepts into easily digestible and engaging learning experiences. At Embedded Prep, he plays a crucial role in building a robust knowledge base that helps learners master the complexities of embedded technologies.